Muscle growth takes time, consistency, and a long-term commitment. But most people can see results with proper strength training and adequate protein intake.
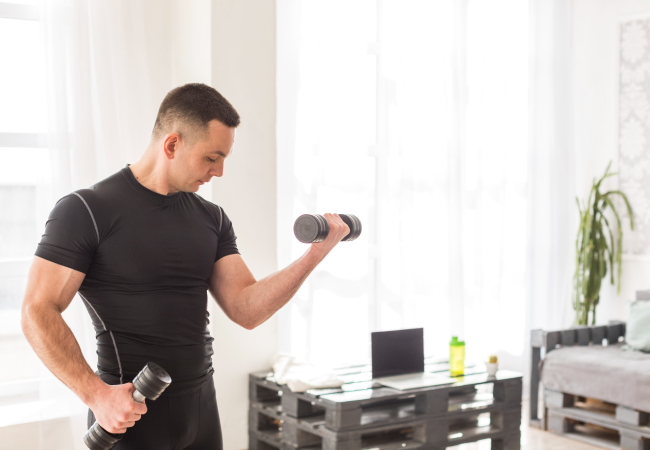
Muscle building is often a top goal for those seeking physique improvement. Added muscle mass improves lean body mass, enhances muscle definition, and adds bulk in all the right areas. This guide covers everything you need to know about how to build muscle, including resistance training, nutrition, and recovery protocols.
The Basics of Muscle Growth

Your skeletal muscles are composed of fibres that contract to produce force. This contraction allows all human movement. Your body constantly recycles amino acids, the building blocks of protein.
You’ll lose muscle mass if your body breaks down more protein than it synthesizes. No change occurs if muscle protein synthesis is balanced. Your muscles grow when your body deposits more protein than it removes.
This increase in muscle mass is called muscle hypertrophy, the primary goal of resistance training. Hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, along with nutrients and amino acids, play a significant role.
To build muscle, the main tools are strength training and adequate protein intake. The correct amount of resistance training triggers a favourable hormonal response for muscle growth. Combined with energy and protein availability, this leads to muscle adaptation and long-term gains.
Tips for How to Build Muscle

The most reliable way to drive muscle hypertrophy is by using your muscles against moderate to heavy resistance. Muscle growth is specific to the muscles being trained.
1. Decide Your Target Number of Repetitions
The repetition continuum is key to designing your muscle-training program.
- 1–5 reps with heavy weights build mostly strength
- 8–12 reps target muscle growth
- 15+ reps improve muscular endurance
Different individuals may respond better to low reps with heavy weight or high reps with light weight. Phases of training using varied reps help optimize muscle protein synthesis.
2. Choose the Right Weight
The weight should be heavy enough to make completing more than 20 reps impossible. You should be near failure by the last repetition.
For example, in a 10-rep set, the tenth rep should be challenging. Avoid leaving more than two reps “in the tank” if your goal is muscle growth.
3. Choose Exercises Wisely
Muscle growth happens in the muscles you actively train. To build bigger biceps, include bicep exercises like curls or compound exercises like pullups.
- Compound exercises: Squats, deadlifts, bench presses. Stimulate multiple muscles, improve functional strength, and maximize workout efficiency.
- Isolation exercises: Target specific muscles, safer for beginners, and help add extra volume after fatigue.
A good mix ensures optimal muscle hypertrophy and overall physique improvement.
4. Structure Workouts to Avoid Overtraining
Perform three sets of 3–5 compound exercises followed by three sets of 1–2 isolation exercises per workout.
Heavier sets are for compound exercises; higher reps are for isolation movements. Limit total exercises to 5–7 per session to maximize gains and reduce muscle fatigue.
5. Training Frequency and Recovery
Muscle recovery is crucial. Train each muscle 2–3 times per week, ensuring proper rest. Overtraining slows muscle adaptation and increases the risk of injury.
Include recovery protocols like sleep, nutrition, and stretching. Adequate protein, calories, and rest enhance muscle fibre growth and muscle mass development.
6. Nutrition for Muscle Growth
Protein is essential for muscle protein synthesis. Include amino acids from lean meats, eggs, dairy, or plant-based sources. Balanced carbs and fats fuel strength training sessions.
Timing meals around workouts can further improve muscle recovery and overall gains.
7. Monitor Progress
Track training intensity, reps and sets, and workout structure. Adjust weights, reps, or exercises to ensure continued muscle growth.
Periodically cycle between moderate weight training, low reps heavy weight, and high reps light weight to keep muscles adapting.
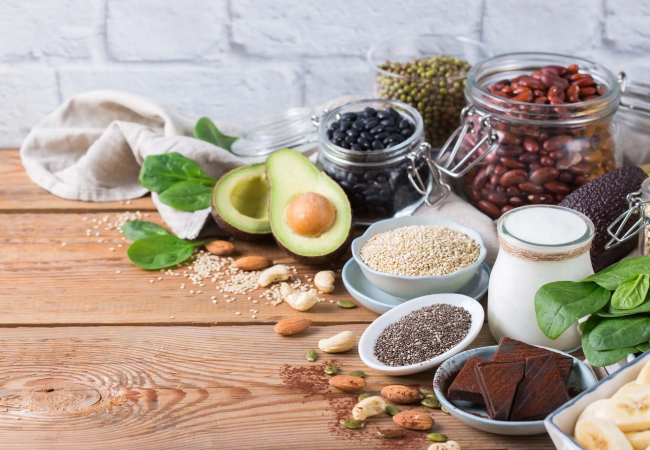
How to Eat to Gain Muscle
Nutrition is the other half of building muscle. All the weight training in the world won’t help if you don’t provide your body with the nutrients it needs to grow new muscle tissue.
Bulking vs. Cutting
Most athletes and serious muscle-building enthusiasts follow a cycle of bulking vs cutting.
- Bulking phase: You eat more calories than you burn to support muscle growth.
- Cutting phase: You restrict calories to reduce body fat while maintaining muscle mass.
During a bulking phase, the goal is to provide enough nutrients for muscle growth without excessive fat gain. A small surplus of 300–500 calories per day is ideal. Beyond this, extra calories are stored as fat. This balance ensures sustainable muscle gain and muscle definition.
Calories Needed to Gain Muscle
To gain muscle effectively, calculate your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). Factors affecting your TDEE include:
- Age
- Sex
- Current lean body mass
- Physical activity
- Occupation
- Underlying medical conditions
Use an online calculator to estimate your baseline needs. Then add 300 calories to set your daily goal. This creates a calorie surplus for muscle gain without excess fat.
Protein Needed to Gain Muscle
Protein is the most essential nutrient for muscle building. Research suggests consuming 1.4–2 grams of protein per kg of body weight per day.
Eat a variety of protein sources for muscle growth, such as:
- Lean cuts of meat
- Low-fat dairy
- Fish
- Eggs
- Nuts
- Plant proteins, including:
- Pea protein
- Soy protein
- Hemp protein
Adequate protein intake supports muscle protein synthesis and enhances muscle hypertrophy during strength training.
Carbs and Fat for Muscle Gain
Carbs provide energy for workouts, while dietary fat supports hormone function and muscle growth.
Research recommends 0.22–0.68 grams of fat per pound (0.5–1.5 grams per kg) of body weight daily. Start at the higher end if you prefer fatty foods and adjust as needed. The rest of your daily calories should come from carbohydrate sources to fuel training and recovery.
Balancing protein, carbs, and fat ensures macronutrient balance for muscle, supports lean body mass, and optimizes nutrient timing for muscle growth.
How Fast Can You Gain Muscle?

Gaining muscle isn’t easy — and it certainly doesn’t happen overnight. Strength training combined with proper nutrition for muscle growth is essential to see results.
Building lean muscle takes months or even years of consistent weight training for muscle and smart eating. Muscle growth rate varies from person to person, even on the same program.
Research from 2020 suggests that adult men can gain 0.5–2 pounds (0.25–0.9 kg) of muscle per month with disciplined strength training and a proper diet. Small monthly gains can add up — over a few years, you could gain 20–40 pounds (9–18 kg) of lean muscle, dramatically changing your physique.
Muscle-Building Foods for Gaining Lean Muscle

Eating the right foods is key to building muscle. Protein for muscle growth and amino acids for muscle help your body respond to strength training. Here’s a detailed list of top muscle-building foods:
1. Eggs
Eggs for muscle building are rich in protein and leucine, a key amino acid for muscle protein synthesis.
Other nutrients include:
- Phospholipids
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Cholesterol
- Vitamin D
2. Salmon
Salmon provides high-quality protein and omega-3 for muscle growth.
Each 3-ounce (85 g) serving contains:
- 17 g protein
- 1.5 g omega-3
- B vitamins for muscle recovery
3. Chicken Breast
Chicken breast is a staple for muscle gain. A 3-ounce serving provides 26.7 g of protein and B vitamins for energy during strength training. Post-workout chicken aids fat loss while promoting lean muscle gain.
4. Greek Yoghurt
Greek Yoghurt contains fast-digesting protein (whey) and slow-digesting protein (casein)—ideal after strength training or before bed to support muscle recovery.
5. Tuna
Tuna contains 20 g of protein per serving, plus vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acids, supporting muscle health and sustainable muscle gain.
6. Lean Beef
Lean beef for muscle provides protein, B vitamins, creatine, and minerals. Choosing 95% lean meat supports muscle mass nutrition without excess fat.
7. Shrimp
Shrimp contains 19 g of protein and high leucine for muscle synthesis. Perfect for lean muscle gain without extra calories.
8. Soybeans
Half a cup provides 16 g of plant protein for muscle and healthy fats. Rich in iron and phosphorus, supporting muscle function.
9. Cottage Cheese
Low-fat cottage cheese packs 28 g of protein per cup and is rich in leucine, which aids muscle protein synthesis and supports strength-training recovery.
10. Turkey Breast
Turkey provides 26 g of protein per 3-ounce serving and niacin for energy processing during muscle-building workouts.
11. Tilapia
Tilapia gives 23 g of protein, vitamin B12, and selenium to enhance strength training performance and muscle growth.
12. Beans
Black, pinto, and kidney beans contain 15 g of protein per cup. Rich in fibre, magnesium, and iron, they support muscle adaptation and sustainable muscle gain.
13. Protein Powders
Protein powders for muscle gain are dietary sources of protein. Whey, casein, soy, pea, beef, and chicken proteins are excellent options.
14. Edamame
One cup provides 18 g of protein and 8 g of fibre; folate and vitamin K support amino acid metabolism for muscle processing and recovery.
15. Quinoa
Quinoa provides 8 g of protein and 40 g of carbs per cup. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function during strength training.
16. Scallops
Scallops give 17 g of protein per 3-ounce serving. Lean and low-calorie, they aid in muscle mass nutrition.
17. Lean Jerky
Lean jerky for muscle is a high-protein, low-fat snack that supports lean muscle growth on the go.
18. Chickpeas
Chickpeas provide 15 g of protein and 45 g of carbs per cup. They are a good plant-based protein source for muscle-building diets.
19. Peanuts
Peanuts have 7 g of protein, 6 g of carbs, and healthy fats per ounce. Useful for extra calories during healthy muscle gain phases.
20. Buckwheat
Buckwheat provides 6 g of protein and is rich in fibre and B vitamins, supporting energy requirements for muscle growth.
21. Tofu
Tofu provides 10 g of protein per half-cup and is rich in calcium. Perfect for plant-based protein to support muscle and muscle function.
22. Pork Tenderloin
Pork tenderloin offers 23 g of protein and only 2 g of fat per 4 ounces, supporting lean muscle gain like beef and chicken.
23. Cow’s Milk
Milk contains fast- and slow-digesting proteins, carbs, and fats. Supports muscle recovery, muscle protein synthesis, and strength training nutrition.
24. Almonds
Almonds provide 6 g of protein per ounce and are rich in vitamin E, magnesium, and phosphorus. They support energy metabolism and muscle recovery.
25. Bison
Bison contains 22 g of protein per 3-ounce serving—a heart-healthy alternative for muscle-building diets.
26. Brown Rice
Brown rice provides 6 g of protein and carbs for resistance training nutrition. Eating carbs before strength training helps your body perform better and stimulate muscle growth.
Foods to Limit or Avoid to Build Muscle

Certain foods and beverages can slow your muscle growth and Progress in strength training. These include:
- Alcohol can interfere with recovery and protein synthesis.
- Ultra-processed foods are low in nutrients and high in empty calories.
- Deep-fried and greasy foods – increase fat storage and reduce nutrient absorption.
- Refined carbohydrates – spike blood sugar without supporting muscle-building nutrition.
- Added sugars – can hinder fat loss and lean muscle gains.
- Sugar-sweetened beverages (like soda) – provide calories with little nutritional value.
Having these foods occasionally won’t ruin your Progress. But for optimal muscle gain, the majority of your calories should come from nutrient-dense, whole foods like lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbs.






Leave a Reply